3D PRINTING
3D Printing is a technology and apparatus for fabricating physical objects directly from parts created in CAD using additive layer manufacturing techniques without manufacturing process planning, tooling or fixture.

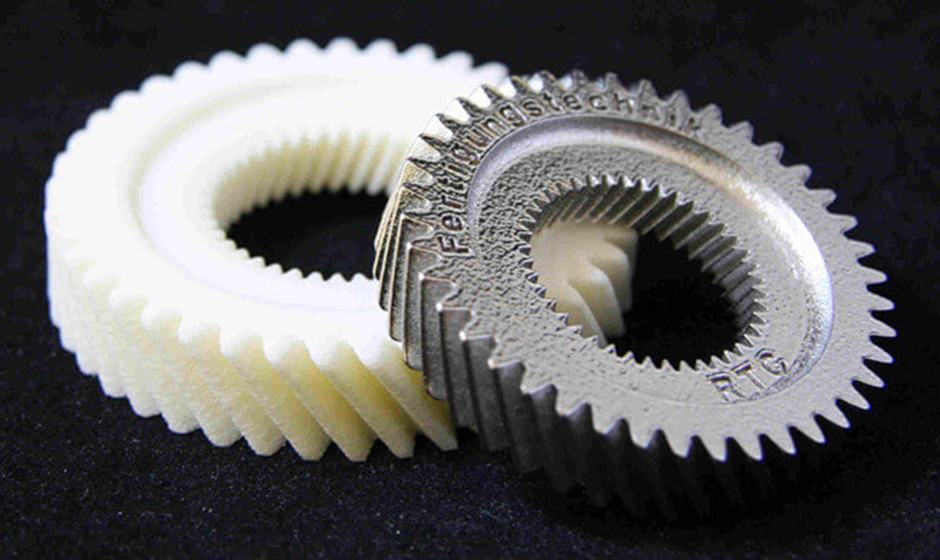

3D PRINTING WORK
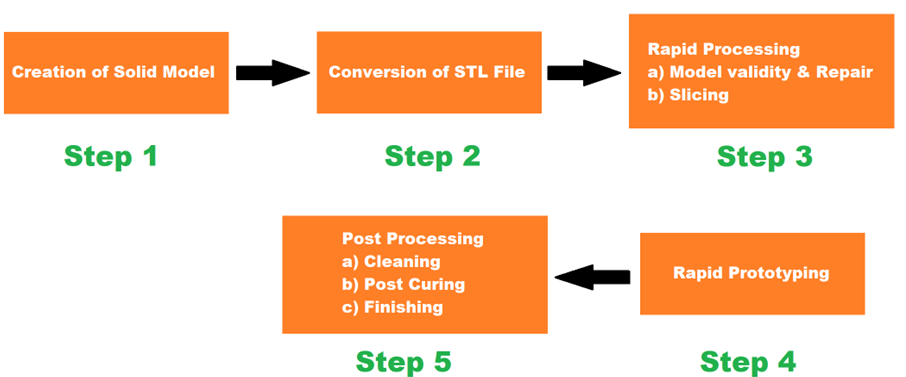
- Rapid Prototyping , also known as 3D printing, is an additive manufacturing technology.
- The 3D printing machine reads the data from the CAD drawing and lays down successive layers of liquid, powder, or sheet materials building up the physical model from a series of cross sections.
- Rapid prototyping services draw upon a number of cutting-edge manufacturing techniques, providing customers with a high-quality full scale prototype within hours once the products design has been conceptualized.
- Rapid prototyping manufacturing sometimes called rapid tooling is a combination of techniques used to quickly create a mold of a part using CAD data.
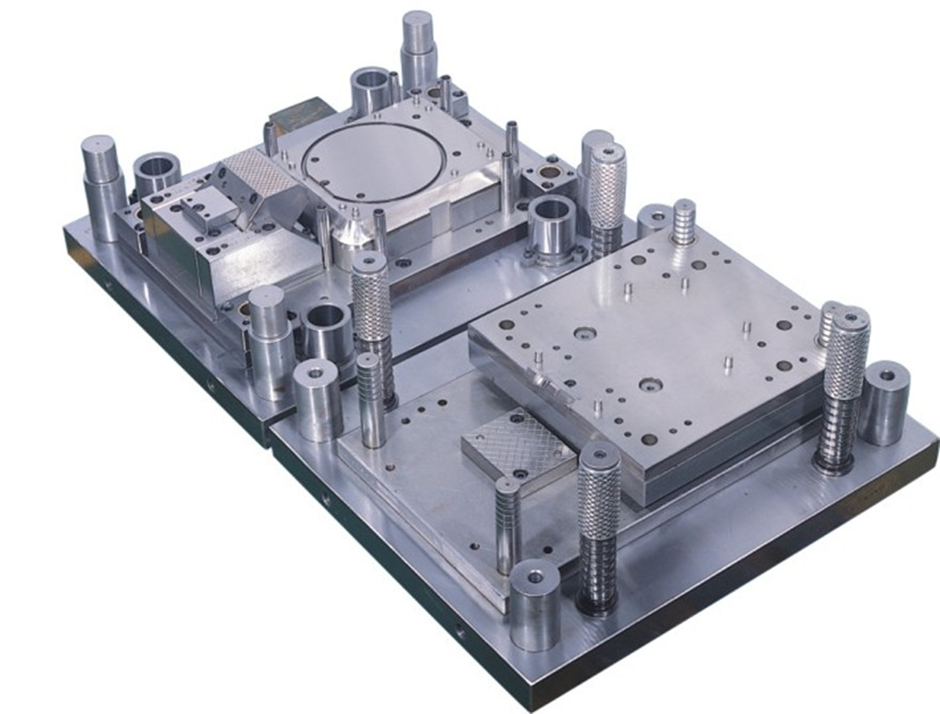
MOLD MAKING
With mold making facilities in house and resources from our partners, we are able to provide plastic injection molds for both rigid plastics and rubbers, metal injection molds for all type of precision stainless steel parts, and pressure die casting molds for aluminum, magnesium and zinc. We offer low-cost local production molds and high-quality exported molds for all your project needs.
TYPES OF MOLDS
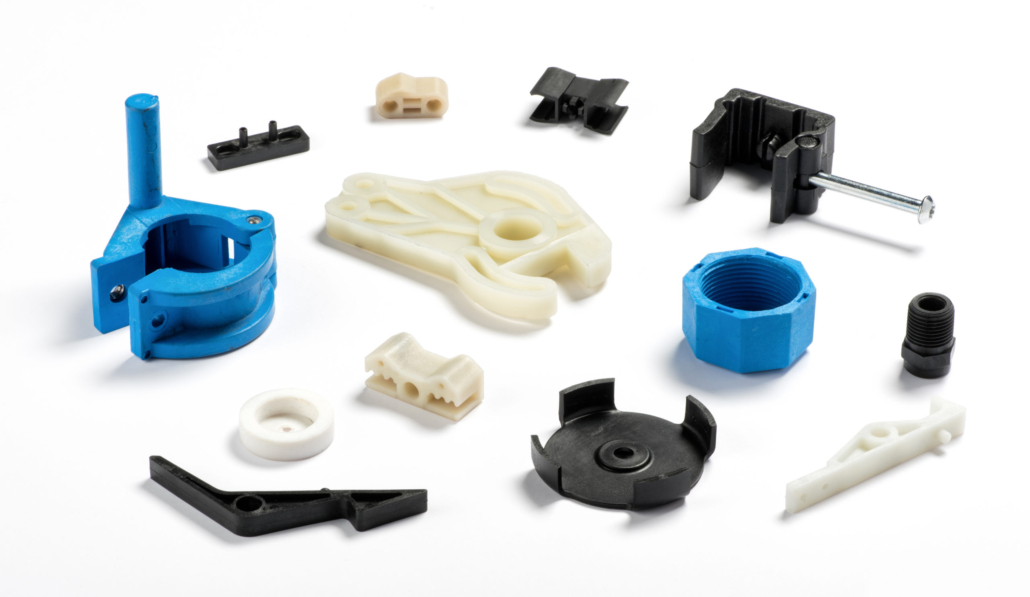
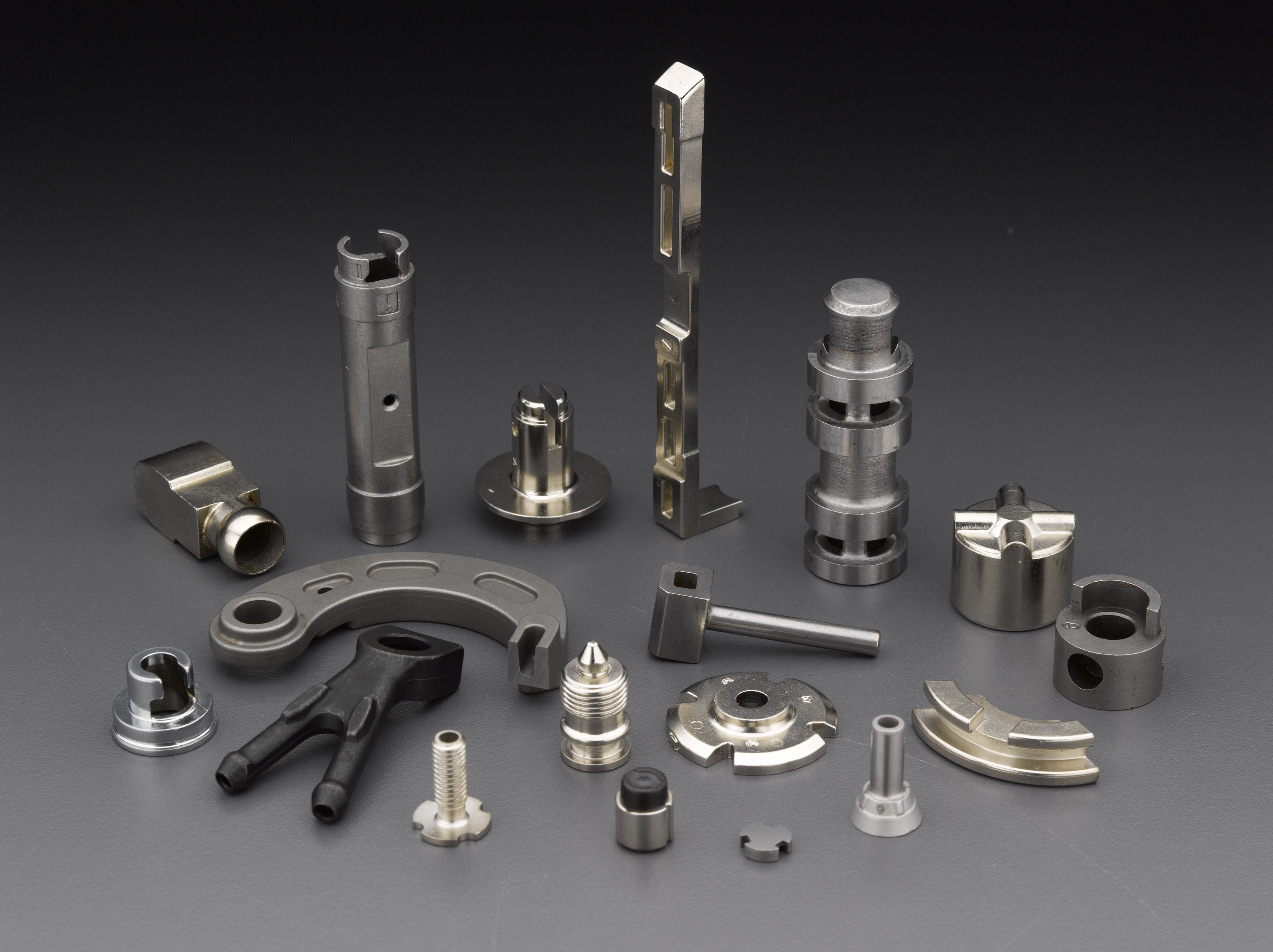
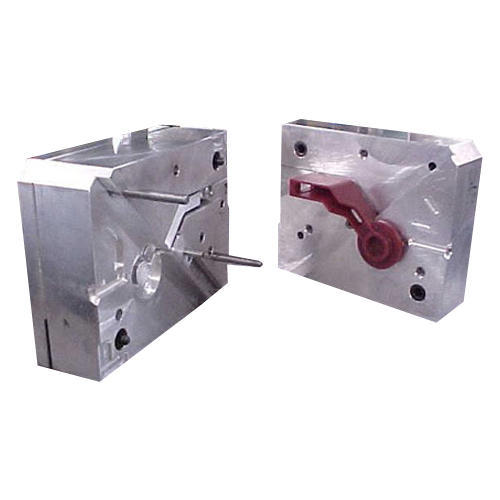





VACUUM CASTING
Vacuum casting or Urethane casting services from CHEMZEST to produce plastic parts to a few hundreds of high quality, textured, coloured & functional parts that ensure that the parts are reliable and suitable for fit and function testing & marketing purposes.
Preparation of Masterpattern
There are three steps to making polyurethane vacuum cast parts: making the master pattern, making molds and casting the parts.
Step 1. Master Patterns
Patterns are 3D solids of your CAD designs. They are usually made by CNC machining or with 3D plastic printing such as SLA/SLS. You can supply your own patterns or we can make them for you. Patterns need to be able to withstand heating to 40°C. A master pattern can be any physical solid of your design.
Step 2. Making the Molds
Casting molds are made from liquid silicone. This silicone is poured around the master pattern inside of a casting box, and then allowed to cure in an oven for 16 hours. Once dried, the mold is cut open and the master removed, leaving behind an empty cavity in the exact negative shape of the original.
Step 3. Casting Copies
Your choice of casting resins can now be poured into the empty cavity to create a highly accurate copy of the original. It’s even possible to overmold with two or more materials. Silicone molds are typically good for 20 or so copies of the master pattern.

